Types of Palletizers and Palletizer Applications
Brief Introduction to Palletizers
What do you do if you need more stackers, material handlers, or machines to stack boxes or bags? One broad word tends to cover it; palletizers. However, there are a few different types of automated palletizers that perform slightly differently in different environments. We understand that NO two facilities are EXACTLY alike - no matter how similar their operation. So we used all of our expertise to bring you a guide to each of them and their use-cases.
Efficient palletizing and pallet configuration is a crucial aspect of many industries, from manufacturing and warehousing to logistics and distribution. The right palletizing system can significantly impact a company's productivity, cost-effectiveness, and overall operations by providing the most efficient throughput and pallet configuration. In this article, we'll delve into the three main types of palletizing systems – industrial palletizers, collaborative palletizers, and conventional palletizers – and explore their unique features and applications.
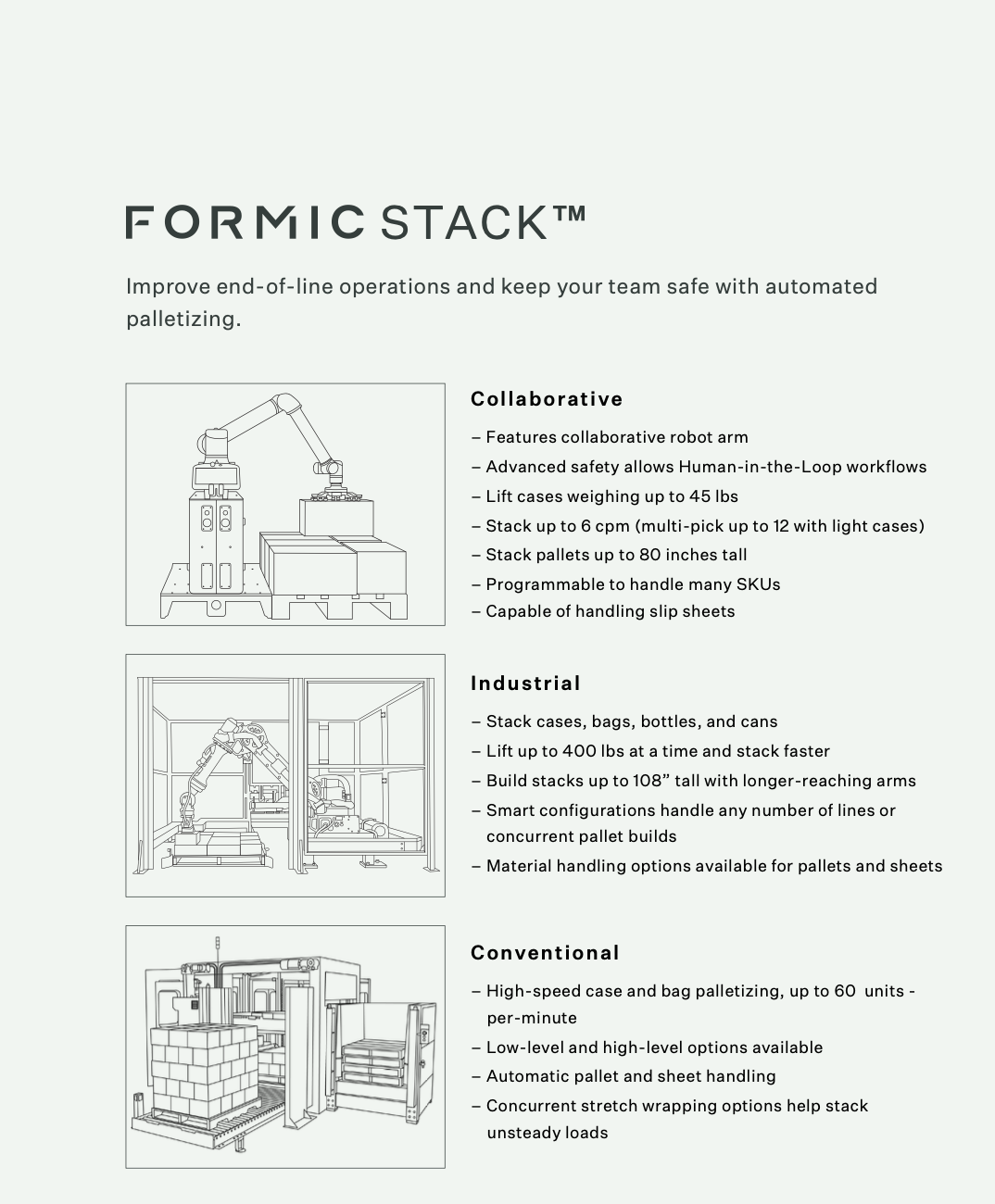
Industrial Palletizers
Industrial palletizers are robotic systems that excel in handling high-speed, heavy-load operations. They are designed for compact palletizing and require minimal maintenance. These machines are ideal for industries that demand high throughput and the stacking of products like bottles, bags, and cases. Here are some key features and applications of industrial palletizers:
Speed and Efficiency
Industrial palletizers are known for their impressive speed and precision, allowing them to stack products at a rapid pace and according to your ideal pallet configuration, making them suitable for high-volume production lines.
Space Efficiency
These palletizers are designed to operate in tight spaces, maximizing floor space usage in a factory or warehouse.
Heavy Load Capacity
Industrial palletizers can handle heavy loads, making them suitable for industries where products are relatively heavy.
Dual-Line Stacking
Many industrial palletizers can stack products from two incoming lines simultaneously, further increasing their efficiency.
Industrial Palletizer Use Cases
Industrial palletizers are commonly used in industries such as beverage bottling, food processing, and manufacturing, where the demand for high-speed stacking and material handling is paramount.
Collaborative Palletizers
Collaborative palletizers, often called cobot palletizers, offer a different approach, focusing on a human-in-the-loop operation. While they may not match the speed of industrial palletizers, cobot palletizers have their own set of advantages, particularly when it comes to flexibility and cost-effectiveness. Here's what you need to know about collaborative palletizers:
Human-In-The-Loop
Collaborative palletizers involve human workers in the stacking process. Staff can place sheets and load pallets alongside the robot, creating a more flexible and adaptable palletizing process and adapting to your preferred pallet configurations.
Case Palletizing
These palletizing cobots are typically used for case palletizing, where the products to be stacked are typically cases or boxes.
Flexibility
Collaborative palletizers can easily be reprogrammed for different tasks, making them ideal for operations that require frequent product line and pallet configuration changes.
Cobot Palletizer Use Cases
Collaborative palletizers (cobot palletizers) are commonly used in industries where speed isn't the primary concern, such as smaller manufacturing operations, warehouses, and distribution centers.
GET YOUR FREE GETTING STARTED GUIDE HERE
Conventional Palletizers
Conventional palletizers, in contrast to robotic systems, rely on mechanical pushers and overhead gantries to arrange products in specific patterns for stacking. These systems often require more space but come with their own unique capabilities:
Pattern-Based Stacking
Conventional palletizers are excellent at arranging products in specific patterns, which is crucial in industries where pallet configuration and stability of the stacked products are important.
Stretch Wrapping
Some conventional palletizers can include stretch wrapping capabilities, further automating the palletizing and packaging process.
Space Requirement
Conventional palletizers generally have a higher space requirement compared to robotic systems, making them more suitable for larger operations with ample floor space.
Conventional Palletizer Use Cases
Industries that rely on conventional palletizers include those dealing with bags, bulk items, and products requiring intricate stacking patterns.
Conclusion
The choice of palletizing system largely depends on the specific needs of a business or industry. Industrial palletizers are the go-to solution for high-speed, heavy-load operations, while collaborative palletizers offer flexibility and cost-effectiveness. Conventional palletizers are ideal for operations that prioritize precise stacking patterns and may have more floor space to spare.
Pallet stacking machines never need to be trained on pallet stacking patterns, how high can you stack boxes on a pallet, and rarely ever make pallet stacking errors.
By understanding the differences between these palletizing systems and their applications, businesses can make informed decisions when selecting vendors and purchasing options to enhance their palletizing operations, streamline production, and improve the overall efficiency of their supply chain. Ultimately, the right palletizing system can contribute significantly to a company's success in the competitive world of manufacturing and logistics.


