At Formic, we deploy both collaborative and industrial/traditional robotic systems depending on the application requirements. We wanted to take a moment to explore collaborative robot technologies, why they’re valuable, and when they’re most appropriate.
What is a collaborative robot?
According to A3 Robotics, a collaborative robot, or cobot, is a type of robot that operates in a hybrid working space shared with humans. With certain safety precautions put in place like environment-sensing software, the cobot is capable of assisting human workers with tedious, repetitive tasks without potentially harming them. To comply with safety standards, the cobot is less capable in handling heavy-duty jobs. However, its ability to work alongside humans greatly reduces the footprint required for deployment and expands the potential use cases of this technology.
The collaborative robot market is already making headway. The market is projected to grow from $1.2 billion in 2021 to $10.5 billion by 2027. With high demand driving market growth, major OEMs are expanding their collaborative portfolio, such as FANUC’s CR series and the Yaskawa Motoman HC series. In turn, the price for these robots has gone down, making them a more viable resource to manufacturers of all sizes.
What are the benefits of collaborative robots?
Safety: Collaborative robots have been designed to comply with safety standards. They are equipped with speed monitoring sensors that can prevent dangerous collisions in the event in which a worker comes too close. For example, there is an “emergency stop” and a “protective stop,” one in which the robot axis brakes, and in the other, the robot slows down. Cobots are also responsible for monitoring the force applied at their end-effector. If it reaches a specific threshold, it immediately stops. The FANUC CR-35iA takes it a step further by covering the body of the robot with a soft rubber material. Overall, safer working conditions improve employee health and reduce operating costs.
Adaptable: Cobots can be easily programmed to deal with changes in a task, without any help from an engineering expert. Employees, regardless of their technical knowledge in robotics, are capable of “training” the robot by simply moving the arms to perform the new task. The cobot quickly learns the process, which gets added to its library of skills. The Universal Robot UR5e-Series is a great example of a robotic solution with an easy-to-use and intuitive interface. A user can simply press arrow keys on a touchscreen tablet to operate and “train” the robot arm.
Delivers ROI quickly: Collaborative robots are proven to deliver faster ROI because of the many factors involved that allow reduced costs. First, cobots don’t need any fencing or extra safety equipment, so users get faster and cheaper integration times. Second, cobots are flexible and capable enough to migrate around a facility and merge into different environments; therefore, more flexibility in use cases. Lastly and the most obvious of the reasons, cobots can work alongside humans, enhancing productivity. At the same time, cobots can run on their own, with zero dependence on the availability of skilled workers.
Common uses of collaborative robots in the manufacturing space:
Material Handling (source: Formic)
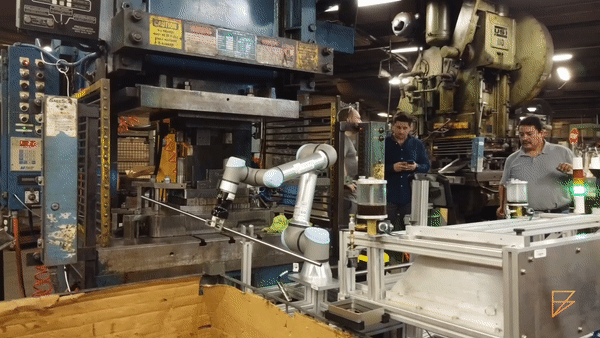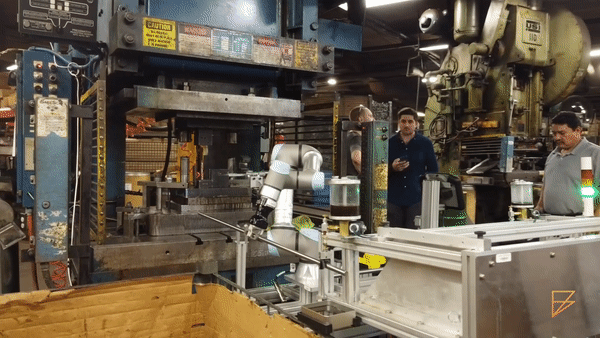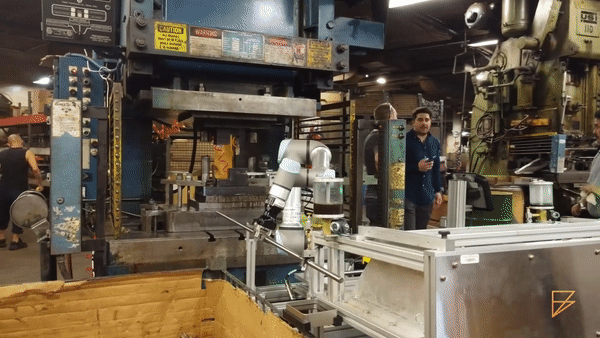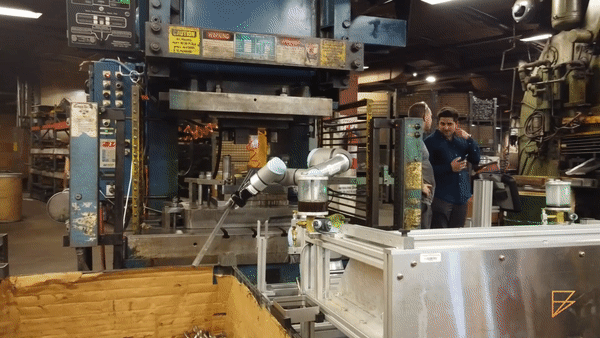
Quality Inspection (source: Rethink Robotics)
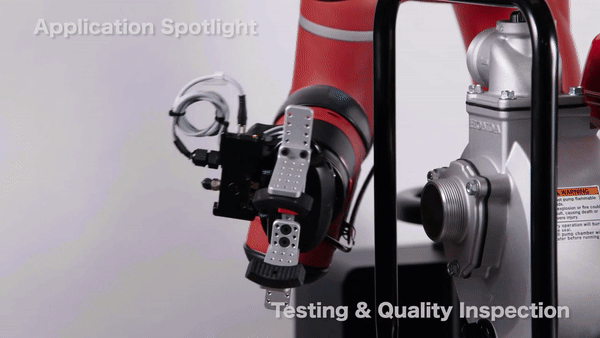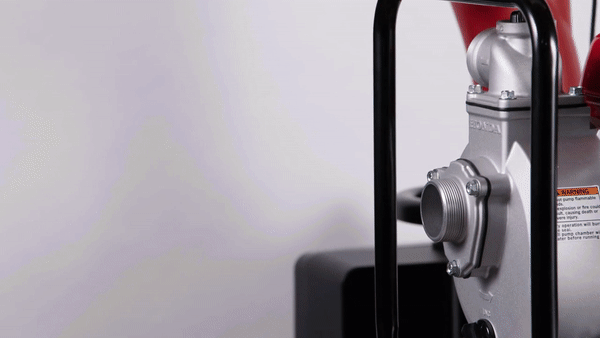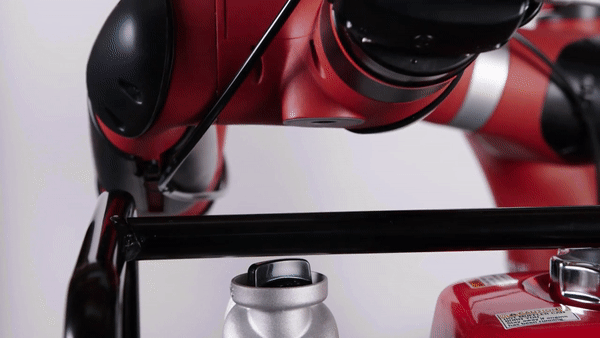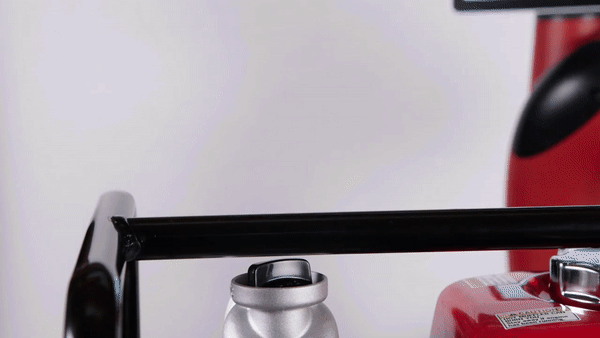
Assembly (source: Tigon Systems)
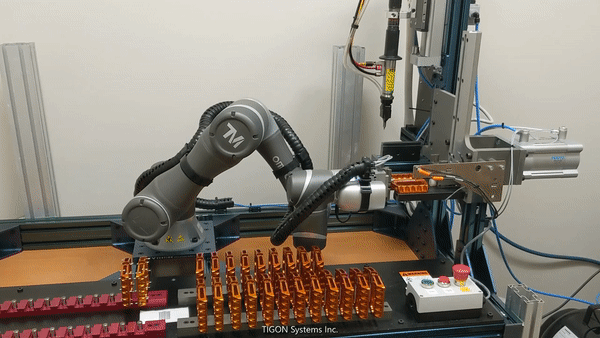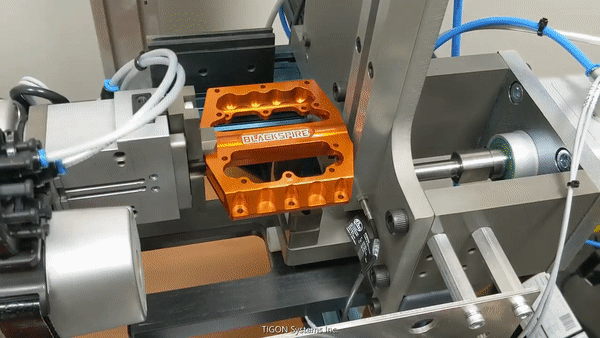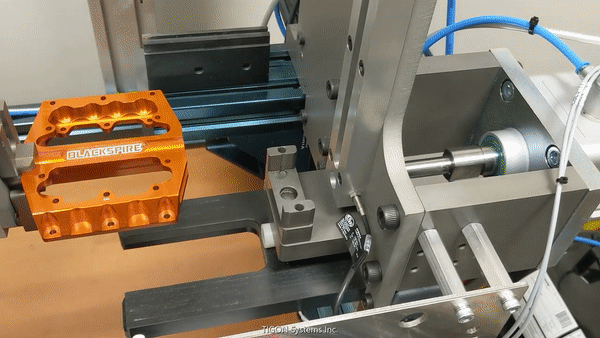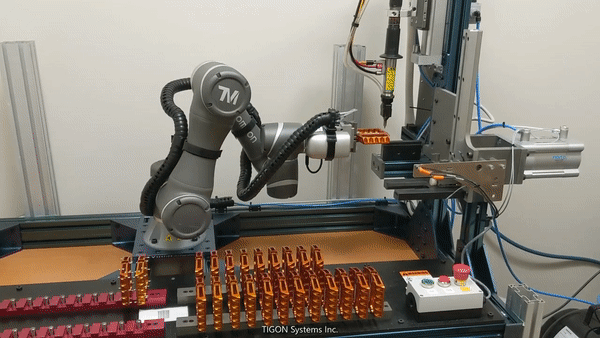
Pick and Place (source: BeaverBot)
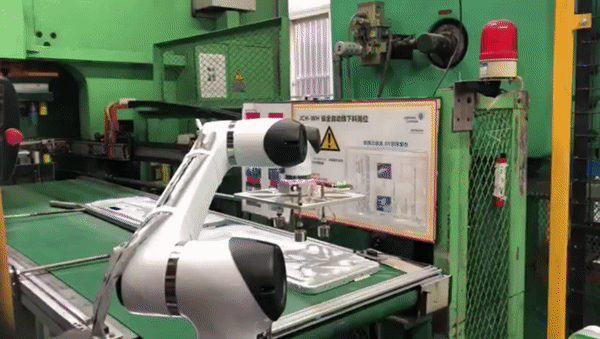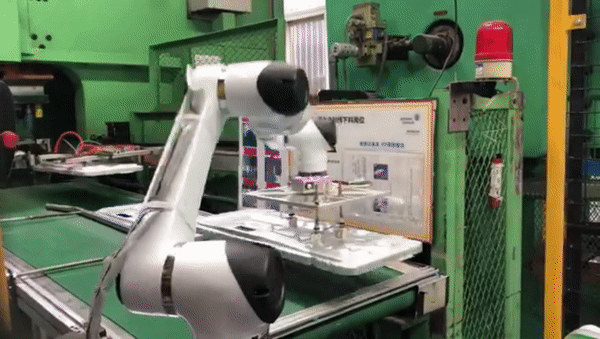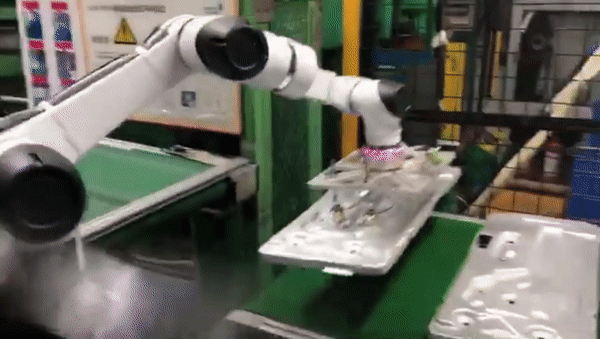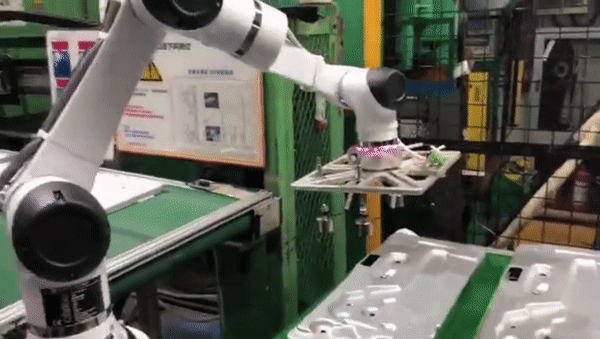
Palletizing

What does the future hold for collaborative robots?
We can expect smarter and more productive collaborative robots in the future. Innovators are improving vision systems to advance their safety measures. There are also new discoveries in gripper technology, like using softer materials to handle delicate objects with greater precision. With further advancements, cobots will become an even stronger resource and partner to the human workforce.


